Spores and their importance in mushroom reproduction
2 years ago · Updated 8 months ago
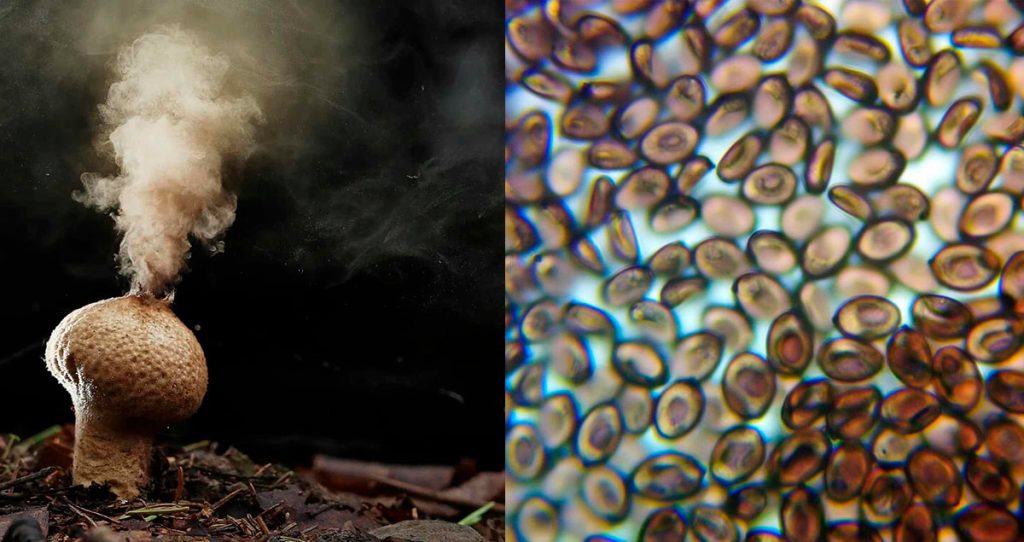
Spores are reproductive cells found in fungi, plants, and bacteria. They participate in reproduction and can withstand adverse environmental conditions. In plants, there are microspores and macrospores. Ferns disperse their spores by wind. Fungi have different types of spores, such as ascospores, basidiospores, and conidia. Bacterial spores form in unfavorable conditions and can provide protection. They are also found in protozoa and are involved in mold growth. Sterilization techniques, such as autoclaving, are used to eliminate them. Chemical disinfectants are not effective against them. 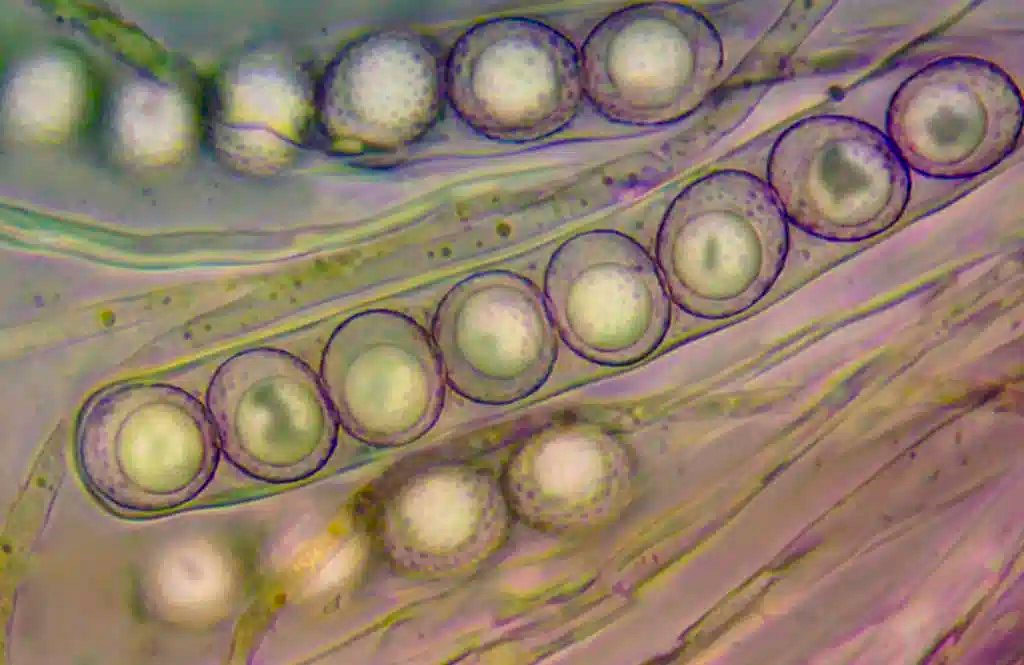
What are spores and what are they for?
Spores are reproductive structures found in certain organisms such as fungi, plants, algae, bacteria, and protozoa. Although they vary in shape and function, their main purpose is to ensure the survival and dispersal of these organisms. Origin and function Spores originate in the reproductive stages of different organisms and play a crucial role in their life cycle. These highly specialized cells can withstand adverse environmental conditions such as high temperatures, humidity, and lack of nutrients. The main function of spores is to enable the propagation of the organisms that produce them. They act as an efficient form of asexual reproduction, as the spore can generate a new individual without the need for fertilization.
Importance of spores in reproduction
Spores play a fundamental role in the reproduction of various organisms. Some plants produce spores as part of their life cycle, allowing new plants to be generated from them. In the case of fungi, spores are key structures in their reproduction process. They can be dispersed by wind, water, and even animal activity, allowing them to reach new places and colonize different environments. Likewise, bacterial spores form under unfavorable conditions as a survival strategy. These spores can withstand hostile environments and, when conditions become favorable again, they germinate and give rise to new bacteria.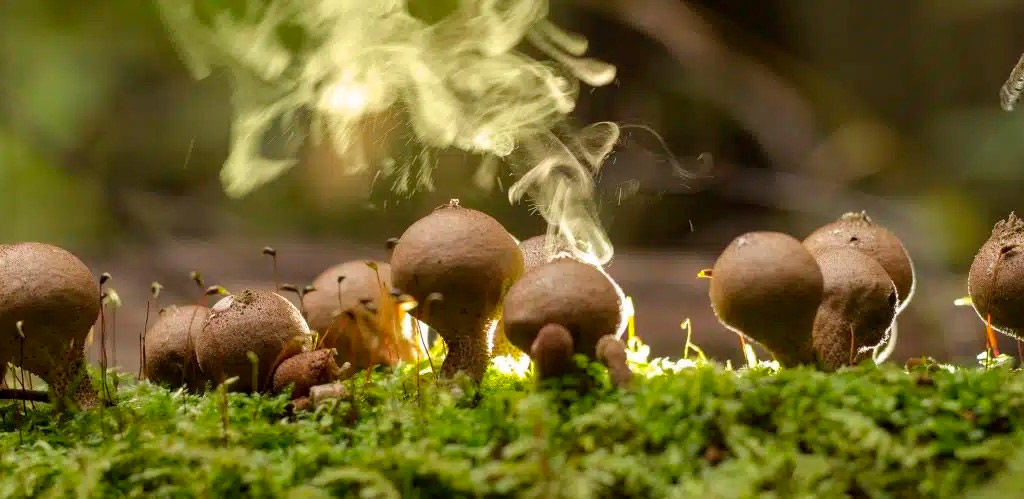 
Types of spores in plant organisms
Spores are reproductive cells present in various plant organisms, playing a fundamental role in their biological cycle. Below, we will explore the different types of spores found in vascular plants, mosses, ferns, and algae, and their importance in reproduction and dispersal.
Spores in vascular plants
Vascular plants, such as trees and shrubs, also produce spores as part of their life cycle. These spores are divided into two main types: microspores and macrospores. Microspores are male spores that develop in reproductive structures called microsporangia, while macrospores are female spores that form in macrosporangia. These spores have specific functions in the reproduction of vascular plants.
Spores in mosses and ferns
Mosses and ferns also produce spores in their reproductive structures. In the case of mosses, spores form in capsules found at the end of the stems. These spores, which are generally small in size, are released into the environment and dispersed by the wind. Ferns, on the other hand, produce spores in structures called sporangia, which are found on the underside of their leaves. These spores are also released into the environment and participate in the reproduction and dispersal of ferns.
Spores in algae
Algae, photosynthetic aquatic organisms, also use spores in their reproduction. These spores form in specialized structures and are released into the water. They can then be transported by ocean and river currents, allowing them to spread and colonize new areas. Algae spores are ecologically important and contribute to the diversity and distribution of these organisms in different aquatic ecosystems. 
Types of spores in fungi and mushrooms
Reproduction in fungi occurs through the production of spores. These spores can vary in shape, function, and mode of reproduction. Below, we will explore the different types of spores and their classification in fungi and pseudofungi.
Spores in fungi and pseudofungi
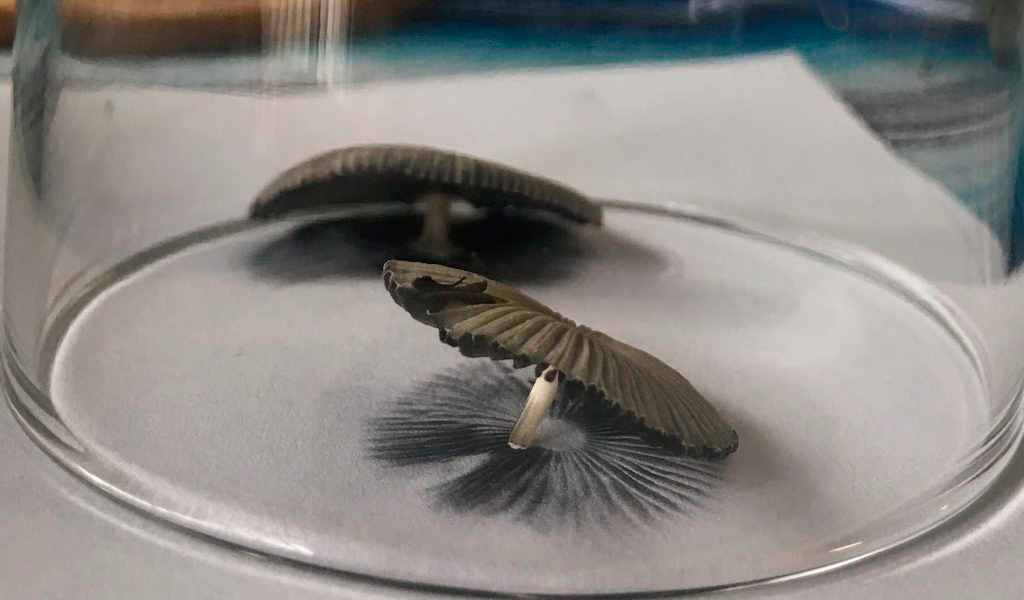
Fungi are organisms that reproduce mainly through their spores. These spores are formed in specialized structures called sporangia, which contain numerous spores inside. Sporangia can be found in both true fungi and pseudofungi. In true fungi, spores develop in structures called basidiospores. These basidiospores form in basidia, which are club-shaped projections found inside mushrooms or fungal fruiting bodies. Each basidium can produce several basidiospores, which are released into the environment to give rise to new individuals. On the other hand, pseudofungi also produce spores, but these are formed differently. Instead of basidiospores, pseudofungi generate oospores. Oospores develop in structures called oosporangia and are usually larger and heavier than basidiospores. Like basidiospores, oospores also have the ability to give rise to new individuals. Classification of spores in fungi Within fungi, spores can be classified into different groups according to their characteristics and mode of reproduction. Some of the most common types of spores in fungi include:
- Ascospores: these spores are found in asci, which are sac-like structures present in fungi of the Ascomycota group. Ascospores are formed through a process of meiosis within the asci and are released into the environment when the asci open. Conidiospores: Conidiospores are asexual spores that form in structures called conidia. These spores are released into the environment and can germinate to give rise to a new fungus. Fungi that produce conidiospores are known as conidial fungi. The classification of spores in fungi can be very broad and varied, as there are numerous groups and subgroups of fungi with distinctive characteristics in their spores. Studying these different types of spores is essential to understanding the various forms of reproduction in fungi and their importance in the life cycle of these organisms. Bacterial spores and their function Formation of bacterial spores Some bacteria have the ability to form spores as a means of defense and survival in unfavorable situations. When environmental conditions become adverse, some bacteria, such as Bacillus clausii, trigger a process of sporulation. During this process, the bacterium forms a protective structure called a spore around its genetic material and other essential components. The formation of bacterial spores is a complex process involving a series of changes in the structure and composition of the bacterial cell. During sporulation, the bacteria undergo an internal remodeling process in which a protective membrane forms around the genetic material and essential nutrients for survival accumulate. Once spore formation is complete, the parent bacterium degrades and the resulting spore remains in a dormant state, protected from unfavorable conditions such as lack of nutrients, high temperatures, or the presence of toxic substances. The bacterial spore can remain in this state for long periods of time, waiting for more favorable conditions to germinate and grow back as an active bacterium.
Importance and risks of bacterial spores
Bacterial spores play a key role in the survival of certain bacteria and can have both beneficial and harmful implications.
- Benefits: Some bacteria, such as Bacillus clausii, use spores as a survival strategy in adverse conditions. In certain contexts, these spores may even have beneficial effects on human health, as they can help promote balance and optimal health in the gut microbiome. In addition, certain bacterial spores have been shown to have antibacterial and antifungal properties. Risks: However, some bacterial spores can pose a risk to human health. Clostridium botulinum, for example, produces spores that can generate the toxin responsible for botulism, a serious and potentially fatal disease. The presence of bacterial spores in food or clinical environments can lead to infections and diseases if proper control and sterilization measures are not taken. It is important to note that bacterial spores are highly resistant and can survive extreme conditions. Their resistance to common chemical disinfectants makes it necessary to implement high-temperature and high-pressure sterilization techniques, such as the use of autoclaves in clinical environments, to completely eliminate the presence of bacterial spores and avoid risks to public health.

Spores in other organisms
Spores in protozoa
Protozoa, a diverse group of single-celled microorganisms, also use spores in their life cycle. These spores, called cysts, allow them to survive in unfavorable environmental conditions. Cysts are resistant structures containing an inactive protozoan cell surrounded by a protective covering. This helps them withstand nutrient deprivation, dehydration, and other environmental stressors. When conditions become favorable again, the cysts germinate and release active protozoa capable of reproducing and continuing their life cycle. Cysts are important for the survival and dispersal of protozoa in different habitats. Spores in mold proliferation Mold, a type of filamentous fungus, also uses spores to reproduce and proliferate. In environments with low light and high humidity, such as bathrooms or dishwashers, mold spores can spread rapidly. These spores are small and light, allowing them to disperse in the air and colonize new surfaces. When environmental conditions are right, mold spores germinate and form new colonies of fungi. This can result in the appearance of mold stains on walls, ceilings, furniture, and other organic materials. To prevent problems associated with mold spores, it is important to ensure good ventilation and control humidity levels in indoor spaces.
- Spores in protozoa are called cysts and allow them to survive in adverse conditions.
- Cysts help protozoa withstand nutrient deprivation, dehydration, and other environmental stressors.
- Under favorable conditions, cysts germinate and release active protozoa capable of reproducing.
Mold, on the other hand, uses spores to spread in environments with low light and high humidity.
- Mold spores are small and light, allowing them to disperse in the air.
- When conditions are right, mold spores germinate and form new colonies of fungi.
- This can result in the appearance of mold stains on different surfaces.
The presence of mold spores can have health implications, as some people may be allergic to them. Therefore, it is important to maintain proper hygiene in indoor spaces and take measures to prevent mold growth.
Importance of sterilization in spore removal
Autoclave sterilization process
Sterilization is an essential procedure for removing spores and ensuring cleanliness in clinical environments and other areas where rigorous microbiological control is required. An autoclave is a machine used in these environments to carry out this process. It consists of subjecting objects and equipment to high temperatures and pressure, which results in the effective destruction of spores and other organisms present. Autoclave sterilization is performed using superheated steam, which penetrates every corner of the object to be sterilized. This high-temperature steam, combined with the pressure generated inside the autoclave, inactivates and eliminates the microbiological spores present. It is a very effective method, as spores are resistant cells and require extreme conditions to be destroyed.
Resistance of spores to chemical disinfectants
Unlike other microorganisms, spores are more resistant to common chemical disinfectants. These cellular structures have thick walls and a protective coating that gives them a high capacity for survival in adverse conditions. The special composition of spores allows them to withstand high temperatures, humidity, chemicals, and other environmental factors that are harmful to most cells. This is why commonly used chemical disinfectants are not sufficient to eliminate them effectively. More rigorous sterilization techniques, such as the use of an autoclave, mentioned above, are necessary.
Some interesting facts about spores
- Extreme resistance: They are specialized reproductive cells that can withstand extreme environmental conditions, such as high temperatures, radiation, dryness, and chemicals. This resistance allows them to survive for long periods of time without germinating. This means that they can generate new plants or individuals without the need for fertilization or the union of sex cells. In fungi: Spores are the main form of reproduction in fungi. When spores mature, they are released into the environment and can grow to form a new fungus if conditions are right. In plants: In plants, spores are produced in structures called sporangia, which are found in the reproductive parts of the plant, such as fern cones. The spores germinate to form a gametophyte, which then produces gametes that fuse to form a new individual. In lichens: Lichens are organisms composed of fungi and algae or cyanobacteria in symbiosis. The spores of fungi in lichens are essential for dispersal and colonization of new substrates. Importance in medicine and food: Some bacterial spores, such as those of the genus Bacillus and Clostridium, can be pathogenic and cause disease in humans. However, they are also used in the production of fermented foods, such as cheese and yogurt. In addition, the spores of some bacteria are used in the manufacture of pharmaceutical products. Study in astrobiology: The resistance of spores to extreme conditions has led them to be considered in astrobiology research. There has been speculation about the possibility that spores could survive in space and be transported between planets, which could have implications for the search for life elsewhere in the universe.
- Diversity of shapes and sizes: Spores can come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes, from microscopic single-celled spores to larger, visible multicellular spores.
These are some interesting facts about spores and their importance in the natural world and scientific research. Cheers and spores!
- Benefits: Some bacteria, such as Bacillus clausii, use spores as a survival strategy in adverse conditions. In certain contexts, these spores may even have beneficial effects on human health, as they can help promote balance and optimal health in the gut microbiome. In addition, certain bacterial spores have been shown to have antibacterial and antifungal properties. Risks: However, some bacterial spores can pose a risk to human health. Clostridium botulinum, for example, produces spores that can generate the toxin responsible for botulism, a serious and potentially fatal disease. The presence of bacterial spores in food or clinical environments can lead to infections and diseases if proper control and sterilization measures are not taken. It is important to note that bacterial spores are highly resistant and can survive extreme conditions. Their resistance to common chemical disinfectants makes it necessary to implement high-temperature and high-pressure sterilization techniques, such as the use of autoclaves in clinical environments, to completely eliminate the presence of bacterial spores and avoid risks to public health.

Te pueden interesar